Approval Matrix Definition: Streamlining Expense Approvals
An approval matrix defines a set of rules that determine who reviews and approves expense reports within your organization. It essentially maps out the approval workflow for expense claims.
Here's a breakdown of the key aspects:
-
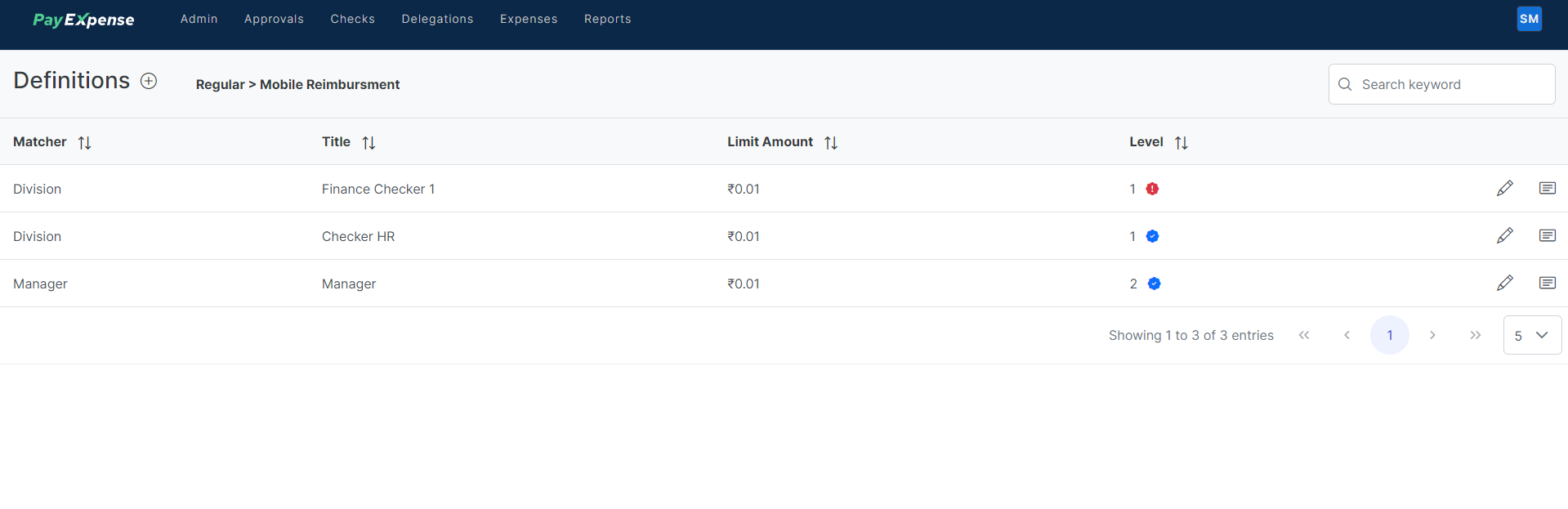
Approval Limits: You can set minimum and maximum spending thresholds for each expense category. Expense reports exceeding these limits require approval from designated individuals.
-
Assigning Approvers: You can designate specific employees to review and approve expense reports. This can be based on factors like department, location, cost center, or employee hierarchy.
-
Approval Workflows: The matrix defines the sequence or structure of the approval process. Here are some common types:
- Sequential Approvals: Expense reports are reviewed and approved by one person at a time, following a predefined order. (e.g., Manager -> Department Head -> Finance)
- Parallel Approvals: Multiple approvers review and approve the report simultaneously. This can be used for specific expense types requiring input from different departments.
- Same Level Parallel or Sequential: Approvals can be set up where multiple individuals at the same level (e.g., Team Leads) need to approve sequentially or simultaneously, depending on your needs.
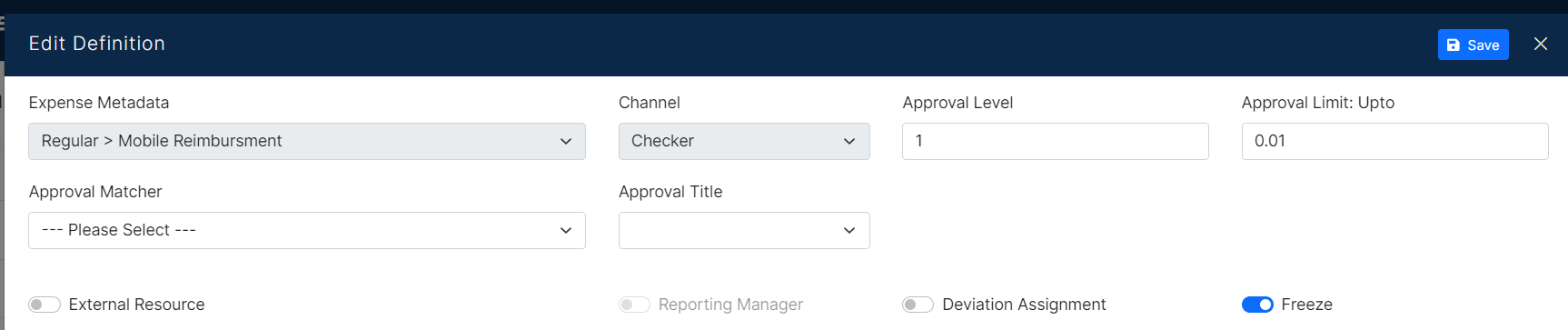
Moreover, admins in PayExpense (or similar expense management systems) can configure deviation rules for additional approvals based on specific scenarios. Here's how it works:
Deviation Rules for Additional Approvals:
- Policy Configuration: Within the policy configuration settings, admins can define criteria that trigger additional approvals beyond the standard approval matrix.
- Common Deviation Triggers: Here are some examples of scenarios that might warrant additional approval:
- Exceeding Spending Limits: If an expense report exceeds the pre-set spending limit for a specific category, the deviation rule can route it to a higher-level approver for review and authorization.
- Policy Exceptions: For certain expense types or situations, the policy might require additional approvals regardless of the amount. Deviation rules can be configured to handle these exceptions.
Benefits of Deviation Rules:
- Enhanced Controls: This functionality provides an extra layer of control over expense approvals, ensuring adherence to spending policies.
- Flexibility: Deviation rules allow for exceptions without compromising the overall approval structure.
- Reduced Risk: By requiring additional approvals for specific scenarios, you can mitigate potential risks associated with non-compliant or excessive expenses.